Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, known as BPH, is a very common, non-cancerous condition causing gradual enlargement of the prostate in men as they mature. BPH rarely causes symptoms before age 40, but half of men between the ages of 51 and 60 and as many as 90% over the age of 80 have symptoms of BPH.
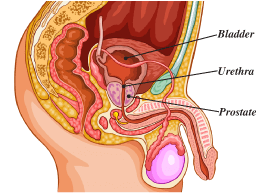
What is the prostate?
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that forms part of the male reproductive system. The prostate produces the fluid that is expressed during ejaculation and is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The prostate also surrounds the urethra which is the canal through which urine passes out of the bladder.
What is the problem?
Problems can arise as the prostate increases in size. As the prostate enlarges, the gland compresses and constricts against the urethra restricting urine flow like a clamp on a garden hose. As a result, the bladder muscle must work harder to push the urine through the compressed urethra, resulting in a thicker, more muscular bladder. As the bladder becomes smaller in capacity and more irritable, leading to the frequent and urgent need to urinate.
Who is at Risk for BPH?
- Men over the age of 50 as the risk for BPH rises with age
- Men whose fathers had BPH
- Men who are overweight or obese
- Men who don’t stay active
- Some men with erectile dysfunction (ED)
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of BPH vary, but the most common symptoms include:
- Weak urinary stream
- Hesitancy or delayed starting
- Increased frequency of urination, especially at night
- Urgency to void, which can progress to leakage
- Possibly bleeding and infection
 Download our free BPH booklet.
Download our free BPH booklet.How is BPH diagnosed?
The diagnosis of BPH is based on both the patients symptoms and physical exam. Often, when BPH is suspected, a man may be referred to an urologish, a doctor who specializes in problems of the urinary tract and the male reproductive system. Various tests and examinations will be performed in the office to accurately evaluate the problem. Learn more.
What is the treatment for BPH?
There are many treatments for BPH. The type of treatment chosen is based on the prostate size, the level of symptoms,and, most important, the desire of the patient to improve his situation. The urologists of UroPartners are experienced in the diagonsis, evaluation, and management of BPH.
Our urologists offer the full range of BPH treatments including medication, the latest proven minimally invasive therapies, such as prostate artery embolization (PAE), the UroLift System, Aquablation and more invasive surgery. We partner with our patients to select the best option for each individual.
Summary
No man is destined to accept the inconvient and life style altering symptoms of BPH as a part of aging. If you are ready to explore which treatment is right for you, please call our office at 630-UROLOGY for an appointment with one of our doctors
To request an appointment online, simply click here.
Related Conditions & Services
Diagnosis of BPHMedical & Minimally Invasive Treatment of BPH
Surgical Treatment of BPH
Some content provided courtesy & permission of the American
Urological Association Foundation, and is current as of 12/2023.
Visit www.urologyhealth.org for additional information.
